Tendons are connective tissues that consist of collagen and connect muscles and bones. They are strong and fibrous, but although they can tolerate stress, they are not unbeatable.
Artificial disc replacement, which is also called vertebral disc arthroplasty, spine arthroplasty or total disc replacement, is a kind of spine surgery that replaces a damaged intervertebral disc with an artificial one. A skilled spine surgeon replaces the affected disc with a metal or metal and plastic device in between the vertebrae. The main aim of artificial disc replacement is getting relief from chronic back pain, restoring disc height, and maintaining spinal flexibility. It is also one of the best alternatives to spinal fusion surgery.
How does artificial disc replacement surgery work?
Most spine surgeons today prefer artificial disc replacement because it is minimally invasive. Here, rather than making an incision in the neck or back, the spine surgeons make tiny incisions in the front part of the body. Then the internal organs are slowly moved to the side to assess the affected disc. This method does not require cutting the muscles, resulting in reduced pain and fast recovery.
After removal of the problematic disc, the lower and upper joint plates are fixed to the spinal endplate bones at the upper edge and lower edge of the damaged disc level. When those plates are in place, the surgeon puts a central core, whose design varies greatly based on different disc implant brands.
While in some, the plates and the core are inserted as one unit, in others, there will be a need to insert the core separately. The function of the central core is to allow movement in between the plates, facilitating bending of the spine and making the spine flexible like a normal disc.
There are several types of artificial disc replacements, and your spine surgeon might modify your vertebral bones present above and below the disc that is removed. With modification, the artificial disc is fixed in a precise position on your spine.
Artificial disc replacement for treating a single level of disease takes somewhere between 45 and 1.15 hours. There might be a requirement to take opioids in lower doses during the initial days of recovery. However, for most people, it’s possible to treat post-surgery discomfort by using acetaminophen, naproxen or th ibuprofen.
Who needs artificial disc replacement?
Artificial disc replacement is suitable for those who have the following conditions:
Degenerative disc disease
It is the natural wear and tear occurring in the intervertebral disc because of aging, physical stress and repetitive movement.
Herniated disc
It is also called bulging disc or protrusion of disc. Here the intervertebral disc lengthens beyond its usual space in the spine. It sometimes pushes into the spinal canal, thereby pinching the nerve present in the lower back or neck, causing back pain or neck pain.
Spinal stenosis
It is narrowing down the spinal canal that decreases the space of the spinal cord or the spinal nerve roots.
Conclusion
Artificial disc replacement is one of the advanced outpatient surgeries where the patients are not required to stay in the hospital. It is important to follow all post-surgery instructions and limit your day-to-day activities for a fast recovery. Physical therapies also help in healing fast and correctly and get all the benefits of artificial disc replacement.
For enquiries and online appointments:
Email – Naveen.st@gmail.com
Call/Whatsapp – +91 7676090119
Visit www.NaveenSpine.com to know more
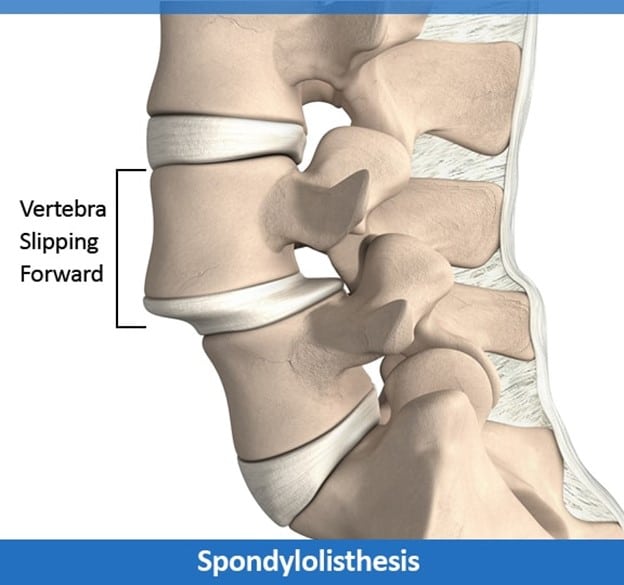
Spondylolisthesis is a condition in which one spinal bone slips from its place and is positioned on the top of the spinal bone present next to it. It commonly happens at the spinal base or the lumbar spine and is called spondylolisthesis of the lumbar spine.
A spinal tumor is an atypical mass of cells within your spinal column or the spinal cord. These cells multiply fast and uncontrollably, unhindered by mechanisms that regulate the growth of normal cells. Spinal tumors can be non-cancerous or cancerous. These spinal tumors can push against the spinal cord and nerve roots, affecting several functions.
Tuberculosis of the spine, or Pott's disease, is one of the infectious diseases that is very rare and results in vertebrae collapse, leading to deformity or hunchback. It is named after Dr. Percivall Pott, the first person to give details about this condition during the 1700s. Spinal tuberculosis, also called tuberculosis spondylitis, forms mainly in the vertebrae and then spreads to nearby areas.
Neck pain is an unavoidable issue that can highly impact a person's overall quality of life. When you have basic understanding of the elaborate relationship that exists between spinal issues and neck pain, it becomes easy to unveil the complicated interplay that surpasses simple discomfort. Let's understand how spinal issues can contribution to neck pain, thereby shedding light on the link between the main support structure of the body and the obstinate ache in the neck.
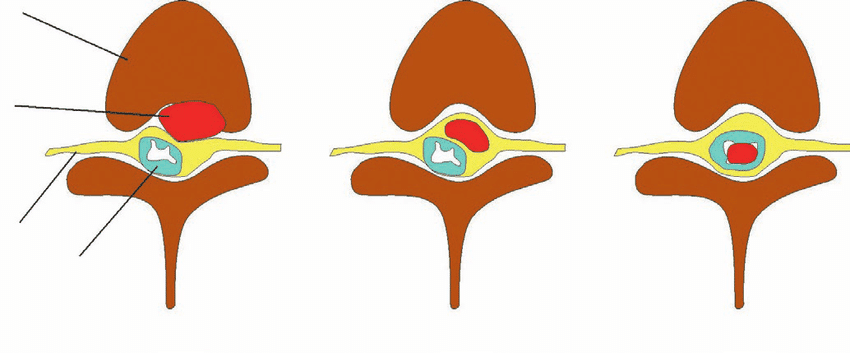
In our spine, in between every bone, there is a disc which serves as a shock absorber and assists in cushioning the bones. But a herniated disc happens when these discs spread outside the capsule holding it and drive towards the spinal canal. A herniated disc can occur anywhere in the spine, including the neck, but mostly, it appears in the lumbar vertebrae or the lower back. The treatment options, generally, include pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, exercise, therapies, rest, and steroid injections. But when all of these treatments fail, herniated disc surgery is the only option.
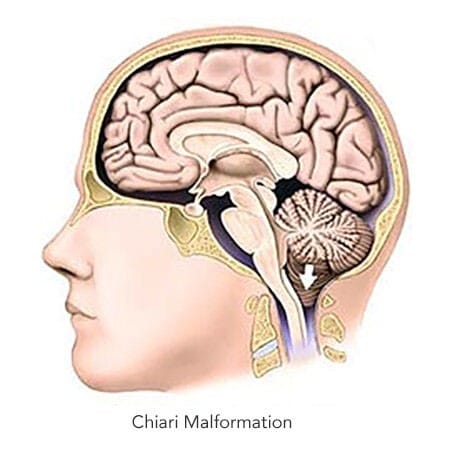
A Chiari malformation is an abnormal growth where the brain tissue in the lower back part of your skull lengthens to your spinal canal. It occurs due to structural issues such as the small size of the skull. When there is no sufficient room in the skull, then part of the brain, mainly the cerebellum, starts growing in the downward direction where there is space at your skull base, known as the foramen magnum.
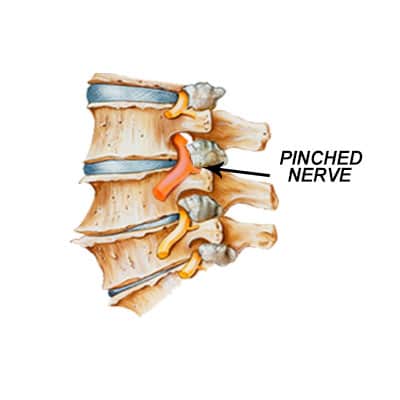
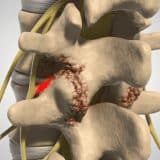
Spinal nerve entrapment, also called pinched nerve or compressed nerve, is a kind of medical condition where a nerve in the spinal cord is compressed, damaged or irritated. It occurs because of pressure from nearby structures, such as bones, herniated discs, ligaments or muscles. This compression can result in several symptoms and discomfort based on the location of the nerve and the cause behind it.
Causes of Spinal nerve entrapment
Herniated discs
Intervertebral discs sometimes become herniated, and the internal gelatinous material of the discs comes out. This causes pressure on the neighboring nerves.
Spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis is when the spinal cord narrows and compresses the spinal nerves. It happens because of aging, any congenital conditions or degenerative causes.
Injuries
Some of the injuries arising from trauma, such as fractures or spinal dislocations, can lead to compression of nerves.
Bone spurs
Also called osteophytes, bone spurs can grow on the spinal vertebrae because of conditions such as osteoarthritis. These bony growths can impinge on the space where the nerves leave the spinal cord, resulting in compression.
Degenerative discs
Ageing can cause the breaking down of the spinal discs, called degenerative discs, thus leading to compression of nerves.
Symptoms
Spinal nerve entrapment symptoms depend on the location of the nerve that is affected. However, here are some of the common symptoms:
- Pain
- Numbness
- Weakness
- Muscle atrophy
- Tingling
The above symptoms might radiate in the nerve path, migrating to other body areas.
Diagnosis and treatment of spinal nerve entrapment
Spinal nerve entrapment is diagnosed by doing a proper physical examination and assessing the patient’s medical history. It also includes medical imaging studies such as X-rays and CT scans for visualization of the spine structures and for pinpointing the source of entrapment.
Treatment of spinal nerve entrapment mainly aims to alleviate its symptoms, reducing the inflammation and addressing the cause. Some of the standard treatment options are:
Resting and modification of activity
Decreasing activities that usually exacerbate the symptoms and facilitating the area that is affected to heal is a significant approach to the treatment of spinal nerve entrapment.
Medicines
Based on severity and condition, doctors often recommend non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines and pain relievers, along with corticosteroid injections.
Surgery
Certain severe cases of nerve compression might need surgical intervention. This involves discectomy, removing herniated disc material, laminectomy or removal of part of the vertebrae to create space for nerves.
The treatment plan mainly depends on the condition, symptoms and cause of the entrapment. Early diagnosis and correct management can result in substantial relief and enhanced life quality for individuals suffering from spinal nerve entrapment.
Conclusion
Nerves extending from the brain and spinal cord send vital messages throughout your body. When you have an entrapped spinal nerve, your body might send signals like pain. So you must pay attention to those body signals, as damages can be severe, sometimes causing long-lasting issues. The earlier you go for diagnosis and start treating nerve compression, the quicker you will get relief from symptoms. Though in many cases, it’s not possible to reverse the whole damage caused by a pinched nerve, timely treatment can help in getting relief from pain and various other symptoms.
For enquiries and online appointments:
Email – Naveen.st@gmail.com
Call/Whatsapp – +91 7676090119
Visit www.NaveenSpine.com to know more
A spinal infection is a rare but severe infection that happens when fungi, viruses or any bacteria enter the spinal tissues. These tiny organisms can affect any part of your spine, from vertebrae to the spinal canal to spinal discs.