Herniated Disc
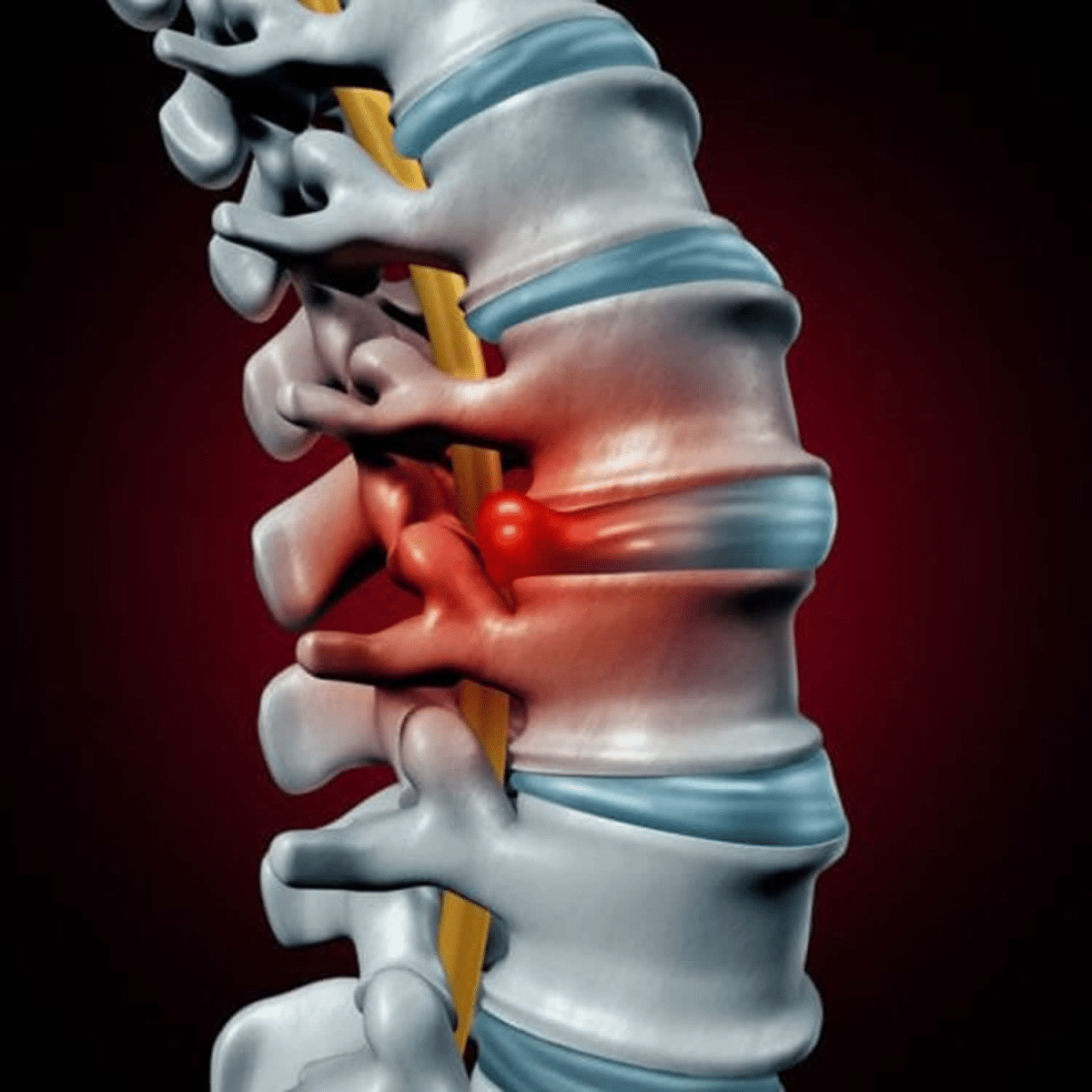
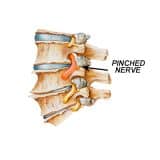
A herniated disc occurs when the spinal disc’s soft center or nucleus comes out from the case. This impacts nerves close to it, causing pain, weakness and numbness in the limbs. But if the disc does not pressure nerves, it will not cause pain. A herniated disc is also called a slipped or bulging disc.
A herniated disc is one of the primary causes of pain in the neck, arm, leg and back. Although it can occur anywhere in the spine, it mostly occurs in the lower neck or back. Very rarely, it occurs in the middle back. People aged 30 years to 50 years mainly get a herniated disc, and it is more common in men than women.
Causes of a herniated disc
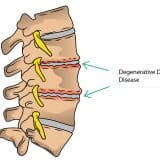
The main cause of herniated disc is slow, age-related wear and tear, known as disc degeneration. With increasing age, the flexibility of discs decreases, and they become more and more prone to tearing, even with small strains or twists.
Many people cannot figure out what caused them to have a herniated disc. Sometimes, using the back muscles rather than the leg and thigh muscles for lifting heavy objects causes herniated discs. A trauma to the back can also lead to a herniated disc.
Herniated disc symptoms
While herniated disc occurs mostly in the lower back, it can also occur in the neck. The symptoms depend on the location of the disc and whether the disc puts pressure on the nerve. Some of the major symptoms of a herniated disc are:
Pain in arm or leg
If the slipped disc is present in your lower neck and causing pain in the region, you will also experience pain in your calf, buttocks and thigh. When the herniated disc is in your neck, there is be pain in your shoulder and arm.
Numbness
People with herniated discs often feel numbness in those parts of the body that the impacted nerve serves.
Weakness
The muscles that are served by the impacted nerve become weak. This causes the inability to lift or hold heavy items.
Although these are some of the common symptoms of a herniated disc, people may have it without any symptoms, too. They can’t know until they see it in the spinal image.
Diagnosis
The healthcare provider does a proper examination to understand the pain, muscle reflexes, muscle strength and sensation. Some of the other tests for diagnosing herniated discs include:
- MRI test
- X Rays
- CT scan
- Electromyogram
Different treatment options for herniated disc
It’s possible to treat herniated discs at home, but you need to consult a doctor if:
- Pain is interfering with your daily life
- Symptoms are not getting better after 4–6 weeks
- There is loss of bowel or bladder control
- You are facing difficulty in walking or standing
Advanced treatments are required if herniated disc symptoms worsen with time. A healthcare provider might give recommendations such as:
Medications
Your doctor might prescribe some pain relievers, muscle relaxants or anti-inflammatory medicines.
Physical therapies
Different physical therapies assist in relieving pressure on nerves and loosening some of the tight muscles and enhancing circulation.
Injections in the spinal cord
A steroid injection given to your spine helps decrease the swelling and inflammation in the affected nerve. This helps your body heal fast so you can return to your daily activities.
Surgery
Herniated disc sometimes causes injury in nerves serving the bladder or bowel. This might need emergency surgery. There are several methods to spinal decompression surgery, but the main goal is relieving the pressure on the nerve.
Conclusion
A herniated disc can make you hesitant to move, making your pain even worse and stiffening your muscles. Remain active and follow all recommendations by your healthcare provider for fast healing. Slow movements, along with some pain relievers, assist people in feeling better in some weeks.
For enquiries and online appointments:
Email – Naveen.st@gmail.com
Call/Whatsapp – +91 7676090119
Visit www.NaveenSpine.com to know more